Mammalian PCR tagging
Warning - if you are accessing the website through a proxy server,
this can lead to the interruption of the connection and the app greys out.
See reference:
CRISPR/Cas12a-assisted PCR tagging of mammalian genes
Julia Fueller, Konrad Herbst, Matthias Meurer, Krisztina Gubicza, Bahtiyar Kurtulmus, Julia D. Knopf,
Daniel Kirrmaier, Benjamin Buchmuller, Gislene Pereira, Marius K. Lemberg, Michael Knop
J Cell Biol (2020) 219 (6): e201910210.
doi:
https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201910210
What is PCR tagging?
- PCR tagging is a one-step procedure for chromosomal gene tagging in mammals
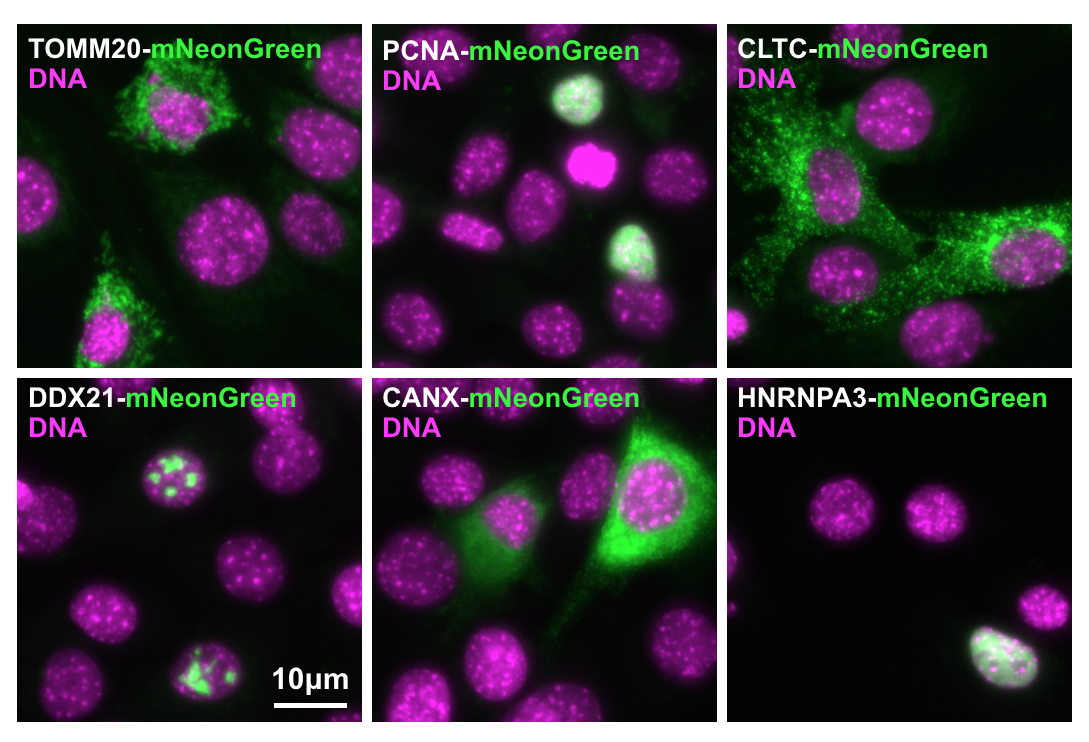
- PCR tagging enables the rapid creation of cell lines with targeted large chromosomal insertions, such as GFP
How does PCR tagging work?
- a gene specific PCR cassette is transfected into the target cells together with a helper plasmid containing a Cas12a endonuclease
- the insertion of the PCR cassette into the chromosome yields a fusion of the tag (e.g. GFP) with the target gene
How is the PCR cassette generated?
- two gene specific tagging oligos (M1 and M2) provide the homology arms (50 to 90 nts in length) for targeted integration by HDR
- the M2 tagging oligo additionally provides a protospacer sequence for the Cas12a endonuclease
- the generic template cassette provides the tag (e.g. a fluorescent protein) and additional features (e.g. a selection marker)
- it also contains the backbone of a Cas12a specific crRNA gene, consisting of promoter and crRNA direct repeat
What is the tagging principle?
- the PCR cassette contains a crRNA gene that is expressed inside the cell
- the crRNA directs Cas12a (expressed from the helper plasmid) to the target locus close to the insertion site
- stimulated by the double strand break the linear tagging cassette is inserted into the genome by HDR
-
the homology arm of the M1 tagging oligo directs in frame fusion of the tag with the target ORF,
leading to the expression of a tagged protein from the target locus - integration leads to destruction of the crRNA target site, thus preventing re-cleavage of the locus
What do I need for PCR tagging?
- the sequence of the target locus (e.g. your favorite gene)
- two tagging oligos (M1 and M2) → design them with our oligo design tool
- two helper plasmids
- a template plasmid with the desired tag, list of PCR cassettes available here
- a Cas12a (Cpf1) expression plasmid for co-transfection, available here , here and here
- a suitable cell line - so far PCR tagging has been shown to work with these cell lines: HEK293T, HeLa, U2OS, RPE-1, mESCs, C2C12-1
How to perform PCR tagging?
- Design M1 and M2 tagging oligos
- Order M1 and M2 tagging oligos
- Run tagging PCR, protocol available here
- Transfect cells
- Select/enrich positive cells
Mammalian PCR tagging
STEP 1: Define your target sequence

STEP 2: Provide a name
This input will be used to generate meaningful names for the oligos.
Please provide a name (e.g. gene name):
STEP 3: Select Cas12a (Cpf1) variant(s)
PCR tagging makes use of published Cas12a (Cpf1) plasmids available from Addgene.
In case you do not have access to all of them, you can unselect the plasmid.
STEP 4: Tagging oligos: define length of homology arms and modification
Please feel free to choose the desired lengths of the homology arms.
We recommend to use 90 nt for the M1 tagging oligo and 55 nt for the M2 tagging oligo.
The current setting limits the oligo length to 120 nt which allows affordable oligo synthesis.
5'-homology arm for the M1 tagging oligo:
3'-homology arm for the M2 tagging oligos:
Number of phosphorothioate bonds:
STEP 5: Compute oligo sequences
The algorithm will search for possible PAM sites in the search space and generate the M1 and M2 tagging oligos as outlined in the image on the right.
RESULTS: Retrieve sequences of M1 and M2 tagging oligos
Mammalian PCR tagging
The pMaCTag plasmids are available at
Addgene
and at
plasmids.eu
If you have any further questions, please feel free to contact the corresponding author,
Michael Knop.
Mammalian PCR tagging
Example protocol for the amplification of the gene tagging PCR cassette
Template:
pMaCTag-Z21
Primer:
M1 and M2 tagging oligos, designed with
our oligo design tool
Expected size:
~ 3.4 kbp
PCR mixture - HiFi polymerase
PCR mixture - Phusion polymerase
PCR mixture - Velocity polymerase
PCR standard program
*HiFi-Polymerase is our self-purified DNA polymerase
10x HiFi buffer - to be used with any polymerase
- 200 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.8
- 100 mM (NH₄)₂SO₄
- 500 mM KCl
- 1% (v/v) Triton X-100
- 1 mg/ml BSA
- 20 mM MgCl₂
We note that the Phusion polymerase using the manufacturer supplied buffer does not work for cassette amplification with M1 and M2 tagging oligos,
whereas for Velocity polymerase using the buffer provided by the manufacturer good amounts of the product are obtained.
We suggest pipetting on ice and pre-heating the PCR machine or hot start.
We found that all polymerases work well using the buffer conditions and amplification above.
Mammalian PCR tagging
Publication about the tagging method
CRISPR/Cas12a-assisted PCR tagging of mammalian genes
Julia Fueller, Konrad Herbst, Matthias Meurer, Krisztina Gubicza, Bahtiyar Kurtulmus, Julia D. Knopf,
Daniel Kirrmaier, Benjamin Buchmuller, Gislene Pereira, Marius K. Lemberg, Michael Knop
J Cell Biol (2020) 219 (6): e201910210.
doi:
https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201910210
References for the online oligo design tool
-
R Core Team (2018). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing Vienna, Austria.
-
Chang W, Cheng J, Allaire JJ, Xie Y, McPherson J (2018). shiny: Web Application Framework for R. R package version 1.1.0.
-
Dean Attali (2018). shinyjs: Easily Improve the User Experience of Your Shiny Apps in Seconds. R package version 1.0.
-
Pages H, Aboyoun P, Gentleman R, DebRoy S (2017). Biostrings: Efficient manipulation of biological strings. R package version 2.46.0.
-
Tóth E et al. (2018). Mb- and FnCpf1 nucleases are active in mammalian cells: activities and PAM preferences of four wild-type Cpf1 nucleases and of their altered PAM specificity variants, Nucleic Acids Research, (i), pp. 1-14. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky815.
-
Kleinstiver B. P. et al. (2019). Engineered CRISPR-Cas12a variants with increased activities and improved targeting ranges for gene, epigenetic and base editing, Nature Biotechnology, p. 1. doi: 10.1038/s41587-018-0011-0.
Disclaimer
The information contained in this website is correct to the best of our knowledge.
Under no circumstance shall the authors be liable for any potential mistakes, claim, damage or loss arising from the use of the application
'Online oligo design tool for PCR tagging in mammalian cells'.
The use of the tool and the reliance on any information on the site is solely at the user's own risk.
Only for non-commercial, academic or research purposes.
Updates
-
21.06.2022 plasmids.eu links added to template list
-
09.09.2020 impLbCas12a added to Cas12a selection
-
04.06.2020 Ensembl ID-based target input now also through our local database possible (no dependence on Ensembl database availability)
-
29.10.2019 Oligo ranking updated - cleavage after STOP codon preferred
-
22.05.2019 Template list completed with Addgene links to mNeonGreen plasmids
-
10.04.2019 Code adjusted to Ensembl 96 release
-
13.03.2019 enAsCas12a added to Cas12a selection
-
21.01.2019 List of species extended for Ensembl Transcript ID input
-
10.01.2019 Template list updated with Addgene links
-
18.12.2018 Human target input enabled also through Ensembl Transcript ID
Bug fixes
-
Fixed bug causing that impLbCas12a PAM-sites were always shown in the result table
-
Fixed forward oligo length when choosing the phosphorothioate modification option
-
Fixed result table showing PAM sites belonging to not chosen Cas12a plasmids
-
Fixed target column in the results of the 17 nt search space after entering a new target
-
Fixed incorrect URL-s in the template list
